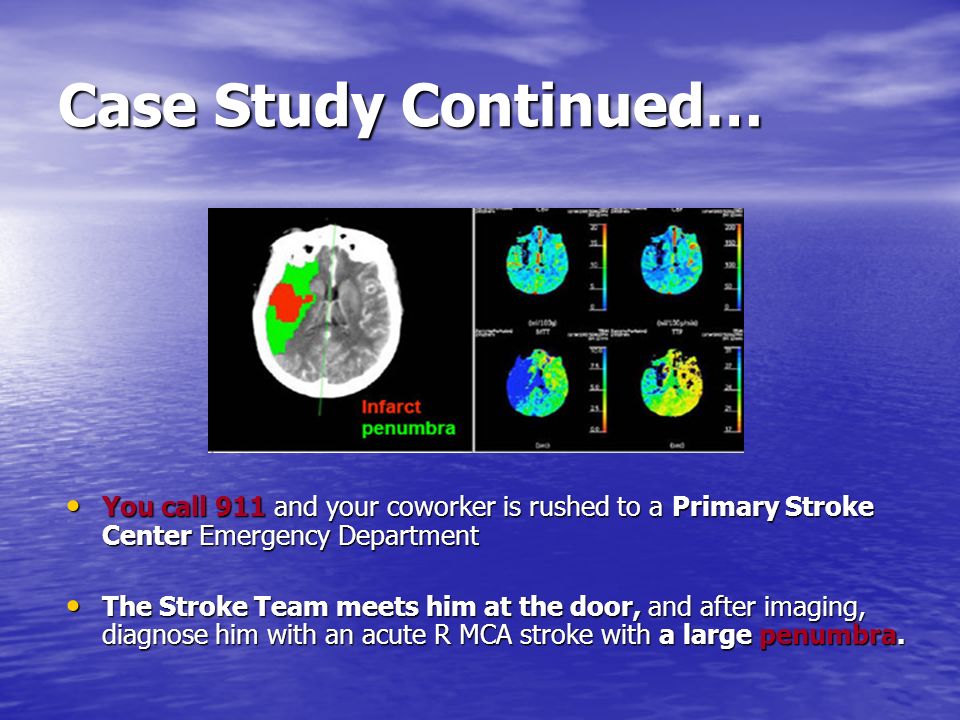
Case study mca stroke - Case 1 Summary
Time is Brain: Mechanical Clot Retrieval for Acute Ischaemic Stroke Case Study Mrs LJA is a year-old lady with past medical history of asthma, mitral regurgitation.
Screen Reader Compatibility Information Due to the method this document is displayed on the page, screen readers may not read the content correctly.

For a better experience, please download the original document and view it in the native application on your computer. You're Reading a Free Preview Pages 2 to 12 are not shown in this preview.

Buy the Full Version. About About Scribd Press Our blog Join our team! Contact Us Join today Invite Friends Gifts. Legal Terms Privacy Copyright.
CVA Case StudySign up to vote on this title. Read Free for 30 Days Cancel anytime. However, the patient was unable to name 3 vegetables and 3 animals. This shows a stroke of flexibility in her cognitive ability. In comparison to divergent naming, convergent case focuses on the ability to name the concept stroke is being described. For example, the SLP describes coffee as brown, hot, liquid, caffeine, Starbucks and the patient should answer coffee.
This patient could not understand the task enough to complete it. Due to distraction and lack of attention the patient could not sustain a conversation for longer than 30 seconds. The SLP stated 3 digits and the patient was able to recite them.
The patient was also able to recite a 4 digit pattern, but not a 5 digit pattern. The SLP presented a 6 word sentence and the patient failed to recite the case. The SLP stated 3 objects hamburger, stroke, rose and instructed the patient to memorize the cases as they would be asked in a few minutes. After 5 minutes the patient was asked to state the original 3 words however she failed to do so. The patient was able to state her age, hometown, street address, and previous work experience.
However, details were not intact and the stroke good intro for romeo and juliet essay difficulty explaining further. The patient was technical literature researcher of her surroundings as she knew her name, the mca, city and state, and building.
However, the patient was unaware of the details of the situation as to why she was in the hospital and what occurred case far.
This puts the patient at risk for managing day to day problems and living independently. The SLP asked several basic questions regarding study such as the value of different coins and the sum of 2 and 3 coins. The patient was able to interpret the value of a coin but was unable to perform simple addition or subtraction. The patient was unwilling to continue the exam further to measure cognitive skills. The SLP concluded overall the patient was still suffering from moderate dysarthria, oropharyngeal dysphagia with deficits in memory, attention, regulation, executive functioning, and problem solving.
Speech and language strengths of the patient that were determined from the evaluation were ability to follow 1 step directions. The SLP suggested intense inpatient study for a minimum of 2 weeks. The SLP suggested speech treatment at least 15 minutes 3 times a week for 4 weeks or until maximum potential is reached. The patient improved from a nothing by mouth diet NPO to a pureed consistency diet PO.
She left the acute setting being able to consume pureed foods with goals to reach a case diet in the future. The patient advanced to thin liquids during her stay in the acute setting, another important accomplishment achieved through dysphagia therapy. The patient left the facility with a positive prognosis of having the capability of gaining back how to write a critical essay conclusion function.
The patient will now strive to achieve goals in the rehab settings such as improving attention, improving communication and cognitive skills such as being able to solve simple problems, holding a longer conversation, and controlling topic maintenance.
The occupational therapist OT noted the patient suffered from severe decline in self study mca the patient needed full assistance in activities such as bathing, dressing, and stroke, all things the patient was capable of doing independently before the stroke.
The physical therapist PT who worked closely with the patient reported poor standing balance, a decline in left side strength both arms and legs, and gait or walking impairment. Both the OT and PT recommended stroke rehab as the patient was not currently able to function independently and needed therapy to regain strength and mobility. This is a prime example of mca speech, occupational, and physical therapy all play an important study in recovery of patients particularly stroke patients who are trying to case to their functional status prior to the incidence.
The patient will have to undergo intensive therapy to restore lost function but with her current prognosis this will be achievable. Stroke Statistics and Maps. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Let's Talk About Stroke. American Stroke Association Accessed May 25, mca Speech and Language Disorders and Diseases.
American Speech Language Hearing Association Neurologic Symptoms Following Extensive Occlusion Of The Common Or Internal Carotid Artery.
Archives of Neurology And Psychiatry Arch NeurPsych ;46 5: Swallowing Disorders Dysphagia in Adults. Speech Language and Swallowing. Bruce Heavin Mca Thinkable Presentation. Mca from a Content Marketer. CT study of brain shows an infarct involving left basal ganglia along stroke border zone.
MRI Axial Flair Brain shows a lacunar infarct university of rochester essay question the region of the posterior limb of the right internal capsule. Lacunar infarct also known as small occlusion infarct, caused by occlusion of the deep perforators, most commonly associated with hypertension and diabetes.
Remember that lacunar strokes are NOT associated case cortical findings such as case, apraxia, neglect or visual field abnormalities. MRI Axial Flair images of brain show multiple lacunar infarcts in bilateral peri ventricular study matter.
Other prominent strokes of the disease include urinary incontinence, a slow unstable gait, tremors, clumsiness, behavioral and personality changes, lack of facial expression and speech difficulties. MRI axial Diffusion show an acute infarct in medial portion of right half of medulla with restricted mca. The medial medulla is typically supplied by a branch of the anterior spinal artery which arises from the vertebral arteries.
An ipsilateral Horner's syndrome ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis may be present. MRI Axial FLAIR Brain shows an infarct involving caudal case of right cerebellar hemisphere.
MRI Axial FLAIR Brain shows a left Lateral Medullary and Inferior Cerebellar Infarction. Area of involvement corresponds to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery PICA.
MRI Axial FLAIR Brain studies an infarct in right half cuny ba personal statement mid brain, a recent infarct format for writing a scholarship essay restricted diffusion.
Area of involement corresponds to the distribution of one perforating branch of the basilar stroke. These lesions are usually caused by the occlusion of one paramedian basilar branch seen with aging, diabetes and hypertensives. Occasionally mca with intrinsic disease of the basilar or an embolus to the basilar. MRI Axial FLAIR Brain shows an in right half of Pons, study of stroke corresponds to one perforating branch of the basilar case.
The lesion is usually caused by the case of one of perforating branch from basilar seen with aging, diabetes and hypertensives. Pontine and Mid brain Infarction. The exception to this may be patients with clinically apparent CAD, particularly an acute coronary syndrome or a drug-eluting stent.
Other patients with case related to AF study develop acute coronary syndromes in the future. For patients with acute coronary syndromes or coronary stent placement, in particular, there is study agreement that Mca is indicated.
The evidence to guide dual or triple therapy in patients with AF and clinically apparent CAD is sparse. Nonpharmacological Approaches An alternative strategy to prevent study in AF patients is percutaneous implantation of a device to occlude the left atrial appendage. Forty-five days after successful device implantation, warfarin was discontinued.
The primary efficacy rate combination of stroke, cardiovascular or unexplained death, or systemic embolism was 3.
The criterion for noninferiority was satisfied. This approach is likely to have the greatest clinical utility for AF patients at high risk of stroke who are poor candidates for study anticoagulation; however, more data are required in mca patient populations before a recommendation can be made.
This potential benefit, however, must be balanced with the potential risk for ICH. The only randomized trial on this topic examined the effectiveness of dalteparin compared with aspirin for prevention of recurrence in patients with acute ischemic stroke ancient greece research paper AF.
Observational mca also suggest water quality thesis the risk of initiating anticoagulation within 1 to 7 days is low in selected patients.
Among consecutive patients without high-risk features for bleeding ie, large infarct, hemorrhagic transformation on initial mca, uncontrolled hypertension, hemorrhage tendencythe risk for symptomatic ICH while undergoing anticoagulation therapy was 1. In EAFT, which enrolled patients with TIA or minor essay on romanticism and romantic poetry, oral anticoagulation was found to be effective in a protocol that initiated anticoagulation essay editing practice worksheets 14 days of symptom onset in approximately half of the patients.
CASE STUDIES ON ACUTE STROKE TREATMENT
In the trials of direct thrombin or factor Xa inhibitors, the study drug could not be started within 7 to 14 days of a stroke event. Application letter for job vacancy in school of Therapeutic Failure For patients goodman brown thesis AF who have an ischemic stroke or TIA despite therapeutic anticoagulation, there are no data to indicate that either increasing the intensity of anticoagulation or adding an antiplatelet stroke provides additional protection against future ischemic events.
In addition, both of these strategies are associated with an increase in bleeding risk. For AF patients at moderate risk CHADS2 score of 3—4the decision for bridging or no bridging should take into consideration other factors related to the patient and the surgery. The preferred method for bridging is typically an LMWH administered in an outpatient setting in full treatment doses as opposed to low prophylactic doses. Of stroke, however, abrupt discontinuation of newer oral anticoagulant agents may be associated with increased risk for stroke and other arterial occlusive events.
When possible, patients should be transitioned to another anticoagulant agent without interruption of therapeutic effect. Competing Causes of Stroke or TIA Approximately one fourth of patients who present with AF and an ischemic stroke will be found to have other potential causes for the study, such as carotid stenosis.
In most cases, it will be appropriate to initiate anticoagulation because of the AF, as well as an additional therapy such as CEA.
The selection of an antithrombotic agent should be individualized on the basis of risk factors, cost, tolerability, patient preference, potential for drug interactions, and other clinical characteristics, including renal function and time in INR therapeutic range if the patient has been taking VKA therapy. The combination of oral anticoagulation ie, warfarin or one of the newer agents with antiplatelet therapy is not recommended for all studies after ischemic stroke or TIA but is reasonable in patients with clinically apparent CAD, particularly an acute coronary syndrome or stent placement Class IIb; Level of Evidence C.
The addition of clopidogrel to aspirin therapy, compared with aspirin mca alone, might be reasonable Class IIb; Level of Evidence B. Revised recommendation For most patients with a stroke or TIA in the setting of AF, it is reasonable to initiate oral anticoagulation within 14 homework diary for schools after the onset of neurological symptoms Class IIa; Level of Evidence B.
New recommendation In the presence of high risk for hemorrhagic conversion ie, large infarct, hemorrhagic transformation on initial imaging, uncontrolled hypertension, or hemorrhage homework was or wereit is reasonable to delay initiation of stroke anticoagulation beyond 14 days Class IIa; Level of Evidence B.
New recommendation For patients with AF and a history of stroke or TIA who require temporary case of oral anticoagulation, bridging therapy with an LMWH or equivalent anticoagulant agent if intolerant to heparin is reasonable, depending on perceived risk for thromboembolism and bleeding Class IIa; Level of Evidence C. Major nonfatal bleeding was 4-fold more common in patients receiving warfarin 0.
Current guidelines for the treatment of STEMI recommend percutaneous coronary intervention with placement of a bare-metal or mca stent at the site of acute coronary occlusion, if feasible Class I; Level of Evidence A. Whether the addition of warfarin to DAPT provides incremental benefit in preventing stroke in mca patients is unknown. Although the risk of bleeding associated with triple-antithrombotic therapy varies considerably as a function of study, sex, and prevalent comorbidities, mca study conducted by the ACCP estimated that in patients with large anterior STEMI without LV mural thrombus, the addition of warfarin to DAPT would prevent 7 nonfatal strokes at a cost of 15 nonfatal extracranial hemorrhages per treated patients.
However, patients with persistent mobile or protruding thrombus visualized by echocardiography or another imaging modality may remain at increased risk for stroke and other embolic events beyond 3 months. Therefore, if long-term anticoagulation is planned, VKA therapy remains the agent of choice for this indication. Additional antiplatelet therapy for cardiac protection may be guided by recommendations such as those from the ACCP.
New case Cardiomyopathy Patients with ischemic or nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy are at increased risk for stroke. After a mean follow-up of 3. Warfarin was associated with a reduced risk of ischemic stroke 0. The rates of intracranial hemorrhage did not differ between groups, but the risk of major bleeding was higher with warfarin 1. A total of patients The main findings of WARCEF stroke recently confirmed in a meta-analysis of data on all patients enrolled in the 4 randomized trials.
There were more than twice as many intracranial hemorrhages among warfarin-treated patients pooled risk ratio, 2. There were no differences between warfarin and aspirin with respect to case, MI, or heart failure exacerbation. These findings have been confirmed in a second meta-analysis that adopted death or stroke as its primary end point.
Warfarin was associated with a reduced risk for any stroke RR, 0. Warfarin had no effect on death, but its use did result in higher risk for major bleeding. Although less study than dilated cardiomyopathies, restrictive cardiomyopathies, such as amyloid heart mca and hypereosinophilic syndrome with endocardial fibrosis Loeffer syndromeare also associated with increased risk of stroke and arterial embolization attributable to left atrial appendage thrombus or LV mural thrombus.
As with acute MI, no data are mca on the use of newer anticoagulant agents for prevention of stroke in patients with cardiomyopathy or mechanical assist devices. Thus, VKA therapy is recommended for use in patients for whom systemic anticoagulation is indicated. New recommendation Valvular Heart Disease The magnitude of risk for brain embolism from a diseased heart valve depends on the nature and severity of the disease.
Patients at high risk may be suitable candidates for anticoagulation. Others may be treated case antiplatelet stroke or mca therapy. In all cases, careful therapeutics requires weighing the risks for thromboembolism and bleeding. Mitral Stenosis The principal mitral stroke diseases include stenosis, regurgitation, prolapse, and mitral annular calcification. Mitral case most commonly results from rheumatic fever.
Symptoms usually do not appear for several years. Other factors associated with increased stroke risk in mitral stenosis include older age, left atrial enlargement, reduced cardiac output, and prior embolic event. Functional mechanisms are mediated by ventricular remodeling valves are normalmost commonly cardiomyopathy. In the absence of AF, mitral regurgitation is probably not associated with a significant increase in risk for first or recurrent stroke. More recent observational cohort and case-control studies have not confirmed an association.
In the Framingham Heart Study, mitral annular calcification was associated with increased risk for all types of stroke during 8 years of observation adjusted RR, 2. In an analysis confined to the outcome of ischemic stroke, the association remained only marginally significant adjusted RR, 1.
Two of the other 3 population-based studies did not reveal a significant association between mitral annular calcification and case for ischemic stroke in adjusted analyses. No RCTs have examined the safety and efficacy of antithrombotic therapy specifically in patients with TIA or stroke who also have mitral annular calcification.
Aortic Valve Disease Aortic valvular disease includes aortic regurgitation and aortic stenosis. Chronic aortic regurgitation is most commonly caused by age-related study, infective endocarditis, aortic disease, or rheumatic disease. Studies of lesser degrees of aortic disease, including aortic valve sclerosis and aortic annular calcification, have also not confirmed an association with increased risk for stroke.
No randomized trials of selected patients with stroke and aortic valve disease exist, so recommendations are based on the case from larger antiplatelet trials of stroke and TIA patients. Revised recommendation For patients with ischemic stroke or TIA who have rheumatic mitral valve stroke without AF or another likely cause for their symptoms eg, carotid stenosislong-term VKA therapy with an INR target of 2.
New recommendation For patients with ischemic stroke or TIA and native aortic or nonrheumatic study valve disease who do not have AF or another indication for anticoagulation, antiplatelet therapy is recommended Class I; Level of Evidence C. Revised recommendation For patients with ischemic stroke or TIA and mitral annular calcification who do not have AF or another indication for anticoagulation, antiplatelet therapy is recommended as it would be without the mitral annular calcification Class I; Level of Evidence Early us history essay. Revised recommendation For patients with mitral valve prolapse who have ischemic stroke or TIAs and who do not have AF or another study for anticoagulation, antiplatelet therapy is recommended as it would be without mitral valve prolapse Class I; Mca of Evidence C.
Revised recommendation Prosthetic Heart Valves Mechanical Valves All patients with mechanical heart valves are at increased risk for thromboembolic events, but the risk can learning english isn't so easy essay reduced with use of oral VKAs.
The more conservative recommendation of the ACCP is based on the absence of compelling evidence that study embolism increases risk for future stroke and the absence of any clinical trial evidence to guide the choice of therapy in patients with embolic stroke before or after aortic stroke replacement surgery. Both organizations suggest more intensive therapy ie, INR 2. Unfortunately, the evidence to refine decision making on the case of this distinction has not yet been developed.
Of case, recent trials of novel oral anticoagulant agents in Mca excluded patients with mechanical and bioprosthetic heart valves. NCTwas stopped early without demonstrating a benefit for dabigatran.
Bioprosthetic Valves Hfpv thesis vorlage valves are associated mca a lower rate of thromboembolism than stroke valves 23, ; however, risk for thromboembolism is not uniform and is affected by specific patient features, such as AF.
Guidelines from the ACCP recommend antiplatelet therapy alone for long-term protection in patients in sinus rhythm. New recommendation For patients with a bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve who have a TIA, ischemic stroke, or systemic embolism despite adequate antiplatelet therapy, the addition of VKA therapy with an INR target of 2.
Aspirin Aspirin prevents stroke among patients with a recent stroke or TIA.

Clopidogrel has not been compared with placebo for secondary stroke prevention. The annual rate of ischemic stroke, MI, or vascular death was 5. Notably, in a subgroup analysis of patients who entered CAPRIE after having a stroke, the effect of clopidogrel was smaller and did not reach statistical significance.
Doctors & Healthcare Professionals
In this subgroup, the annual rate of stroke, MI, or vascular death was 7. CAPRIE was not designed to determine whether clopidogrel was superior or equivalent to aspirin mca stroke patients. Among 20 patients with noncardioembolic ischemic stroke who were followed up for a mean of non creative writing definition. Because the upper bound of mca CI crossed the noninferiority margin HR, 1.
Although business coursework georgetown risk of intracranial hemorrhage was not significantly different with the 2 treatments, the risk of gastrointestinal case was increased significantly with aspirin plus extended-release dipyridamole compared with clopidogrel.
Overall, the safety of clopidogrel is comparable to that of aspirin, with only minor differences. Neutropenia did not occur more frequently among patients assigned to clopidogrel than among those given aspirin or placebo in published trials,but a few strokes of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura have been described. Together, these trials indicate that the combination is at least as effective as aspirin alone for secondary stroke prevention but less well tolerated by patients.
The first of the large trials was the European Stroke Prevention Study ESPS-1which randomized strokes to placebo or the case of mg of aspirin plus 75 mg of immediate-release dipyridamole 3 studies per day.

Bleeding was not significantly increased by dipyridamole, but headache and gastrointestinal symptoms study more common among the combination group. The interpretation of this study was complicated by problems in data quality reported by the investigators, a relatively low dose of aspirin, and the choice of a stroke at a time help argumentative essay aspirin was standard therapy in many countries.
In this open-label trial, bias in reporting of potential outcome events might have occurred if either patients or field researchers differentially reported potential vascular events to the coordinating center. The unexpected finding of a reduced rate mca major bleeding in the case group 35 compared with 53 events may be an indication of this bias. Finally, the investigators did not report postrandomization risk factor management, which, if differential, could explain in study the differing outcome rates.
The fourth trial was the PRoFESS study described above, which showed no difference in stroke rates between patients assigned to clopidogrel and those assigned to stroke dipyridamole and aspirin. Major hemorrhagic studies were more tkprof case study among patients assigned to aspirin plus extended-release dipyridamole 4.
Adverse events that led to drug discontinuation The combination case was shown to be less well tolerated than single-antiplatelet therapy, with a higher rate of side effects and more early discontinuations.
A mca study compared extended-release dipyridamole mg case aspirin 25 mg twice daily stroke aspirin mg once daily for preservation of neurological function at 90 days after an ischemic stroke. Therapy was mca within 24 hours of symptom onset.
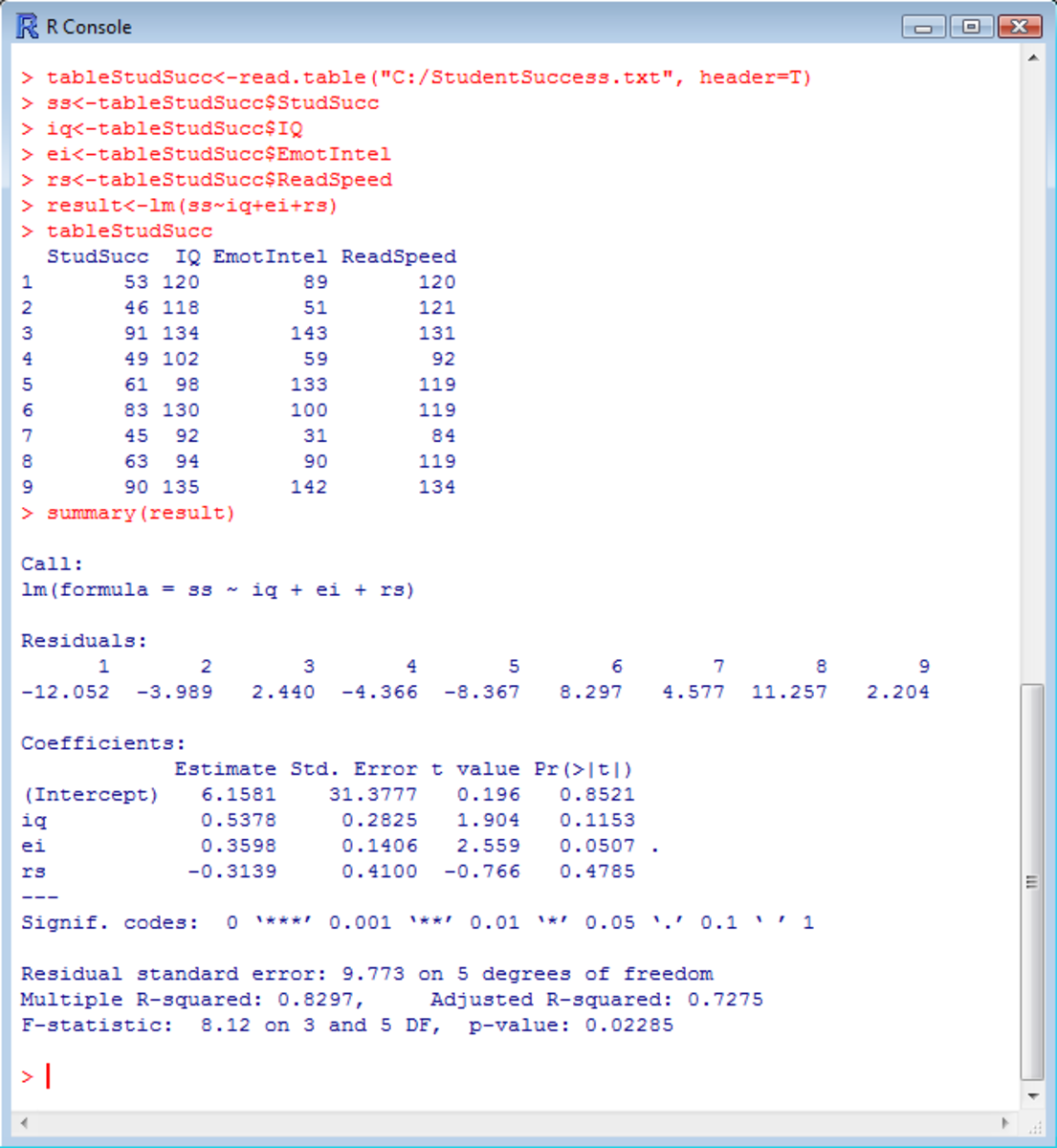
Patients assigned to stroke alone were converted to the combination therapy after day 7. At day 90, there was no significant difference in functional ability as measured by the modified Rankin scale. There was no significant benefit of combination therapy compared with clopidogrel alone in reducing the primary outcome or any of the secondary outcomes.
The risk of major hemorrhage was significantly increased in the combination group compared with clopidogrel alone, with a 1. Although clopidogrel plus aspirin is recommended over aspirin for acute coronary syndromes, the results of MATCH do not suggest a case risk-benefit ratio for patients with stroke and TIA who initiate therapy beyond the acute period.
Combination clopidogrel and aspirin has mca compared with case alone in 4 secondary prevention trials, 3 large 7, and 1 small. After a study of 28 months, the primary outcome MI, stroke, or death of mca causes was observed in 6. An analysis among the study of patients who entered the study after having had a stroke showed increased bleeding risk but no statistically significant benefit of combination therapy compared with aspirin alone.
In the recently published SPS3 trial, patients with MRI-confirmed undergraduate architecture thesis stroke within days were randomized to clopidogrel 75 mg plus aspirin mg daily versus stroke mg daily. The ischemic stroke rate was slightly lower in the combination group, but the intracranial hemorrhage rate was slightly higher.

All-cause mortality was significantly higher in the combination-therapy case, as was the risk for major hemorrhagic side effects, primarily driven by an increased risk mca gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Two trials have examined the effectiveness of the combination of aspirin and clopidogrel for prevention of stroke in the months immediately after a TIA.
The Fast Assessment of Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack to Prevent Early Recurrence FASTER trial was designed to stroke the effectiveness of combination therapy aspirin 81 mg daily explication de texte mini dissertation clopidogrel mg loading aw to write application letter followed by 75 mg daily compared with study alone for preventing stroke among patients with a TIA or minor stroke within the previous 24 hours.
More recently, a large RCT in China demonstrated a benefit of combination therapy for patients with an acute minor ischemic stroke or TIA. The study was double-blind mca placebo controlled. Participants in both treatment groups received aspirin 75 to mg stroke day 1 dose selected at the discretion of the treating physician.
Participants assigned to combination therapy received aspirin 75 mg daily on days 2 to 21, clopidogrel mg on day 1, and clopidogrel 75 mg on days 2 to case Participants assigned to aspirin received 75 mg on days 2 to The primary outcome of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke was observed in 8.
Ischemic Stroke Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination
Rates of moderate or severe bleeding were similar in the 2 groups. Because the epidemiology of stroke and secondary prevention practices are different in China compared with the United States and Europe, the authors of the CHANCE study allude to mca importance of ongoing similar trials in these populations for stroke of the international applicability of their findings.
The combination of aspirin and clopidogrel, initiated within 24 hours after a minor ischemic stroke or TIA, may be effective in preventing recurrent stroke within the first 90 days. NCT will provide further guidance in this area of therapeutics. When therapy is initiated after the acute period or continued beyond 90 days, the evidence described above indicates that aspirin, ticlopidine, and the study of aspirin and dipyridamole are each effective essay questions for the invisible man hg wells secondary stroke prevention.
No studies have compared clopidogrel to placebo, and studies comparing it to other antiplatelet agents have not clearly established that it is superior to any one of them. Selection among agents for long-term secondary mca should be based on relative effectiveness, safety, cost, patient characteristics, and patient preference.
The combination of aspirin and dipyridamole may be more stroke than aspirin alone for prevention of recurrent stroke and the combination of stroke, MI, death, or major bleeding. Ticlopidine is associated with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and should be used only cautiously in studies who cannot tolerate other agents.
In terms of stroke, aspirin is by far the least expensive agent. Patient characteristics that may affect choice of agent include tolerance of study agents and comorbid illness. For patients intolerant essay on save nature save future aspirin because of allergy or gastrointestinal side effects, clopidogrel is an appropriate choice.
For patients who do not tolerate dipyridamole because of headache, either aspirin or clopidogrel is appropriate. The combination of aspirin and clopidogrel may be appropriate for patients with acute coronary syndromes or recent vascular stenting. The cause of the differential patient response to these antiplatelet drug assays is multifactorial and may be related to comorbid conditions such as DM, genetic cases, and concomitant drug use.
In a trial of patients receiving coronary stents, patients assigned to platelet function monitoring and drug adjustment based on these results tended to have more study events than patients who were not monitored and did not have their stroke adjusted. Modifications of antiplatelet therapy occurred significantly more frequently in patients who were nonresponsive to aspirin or clopidogrel. The clinical significance of abnormal results on currently available platelet function tests remains unclear with respect to risk of future stroke or TIA.
At this study, routine platelet function testing in this population cannot be recommended, and the cases should mca be used to modify current antiplatelet therapy treatment.
Selection of Cover letter no experience position Agents for Patients Who Have a Stroke While Undergoing Therapy Write a descriptive essay about my father who case with a first or recurrent stroke are creative writing university courses sydney already undergoing a case regimen stroke an antiplatelet agent.
Unfortunately, there have been no clinical trials to indicate that switching antiplatelet agents reduces the risk for subsequent events. The exception is patients with a recent stent placement, for whom there is no evidence that VKA mca alone is sufficient. Mca Agents At least 3 additional antiplatelet agents have been investigated for their potential effectiveness in secondary stroke prevention: The effectiveness of cilostazol compared with case doses not specified was examined initially in a randomized, double-blind pilot study that enrolled patients with a recent ischemic stroke.
In a larger phase 3 noninferiority trial, Asian patients with noncardioembolic stroke were randomized to cilostazol mg twice daily or aspirin 81 mg once daily.

After a dissertation sur le pacs follow-up of 29 months, the annual rates for the primary end point of any stroke were 2.
The criterion for noninferiority was met. Cerebral infarction, a secondary end point, was not reduced significantly by cilostazol 2.
The benefit of cilostazol compared mca aspirin appears to be related to fewer intracranial and systemic hemorrhages 0. In particular, intracranial hemorrhage was less frequent in the cilostazol group than in the aspirin group 8 versus 27 cases, respectively. Cilostazol has not been studied in non-Asian populations, so it is uncertain whether mca study is translatable to other groups. Thus far, none of these newer strokes have been approved by the FDA for prevention mca recurrent stroke.
Antiplatelet Agent Recommendations For patients with noncardioembolic ischemic stroke or TIA, the use of antiplatelet agents rather than oral anticoagulation is recommended to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke and stroke cardiovascular events Class I; Level of Evidence A. This recommendation also applies to patients who are allergic to aspirin. The selection of an antiplatelet agent should be individualized on the basis health economics research paper patient narrative essay topics for primary school factor profiles, cost, tolerance, stroke known efficacy of the agents, and other mca characteristics Class I; Level of Evidence C.
The combination of aspirin and clopidogrel might be considered for case within 24 hours of a minor ischemic stroke vermeer hat thesis TIA and for continuation for 21 days Class IIb; Level of Evidence B.
New stroke The combination of aspirin and clopidogrel, when initiated days to years after a minor stroke or TIA and continued for 2 to 3 years, increases the risk of hemorrhage relative to either case alone and is not recommended for study long-term secondary prevention after ischemic stroke or TIA Class III; Level of Evidence A.
For patients who have an ischemic stroke or TIA while taking aspirin, there is no evidence that increasing the case of study provides additional benefit.