Critical thinking in science education
International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Vol. 1 No. 17 [Special Issue – November ] Critical Thinking Theory and Nursing Education.
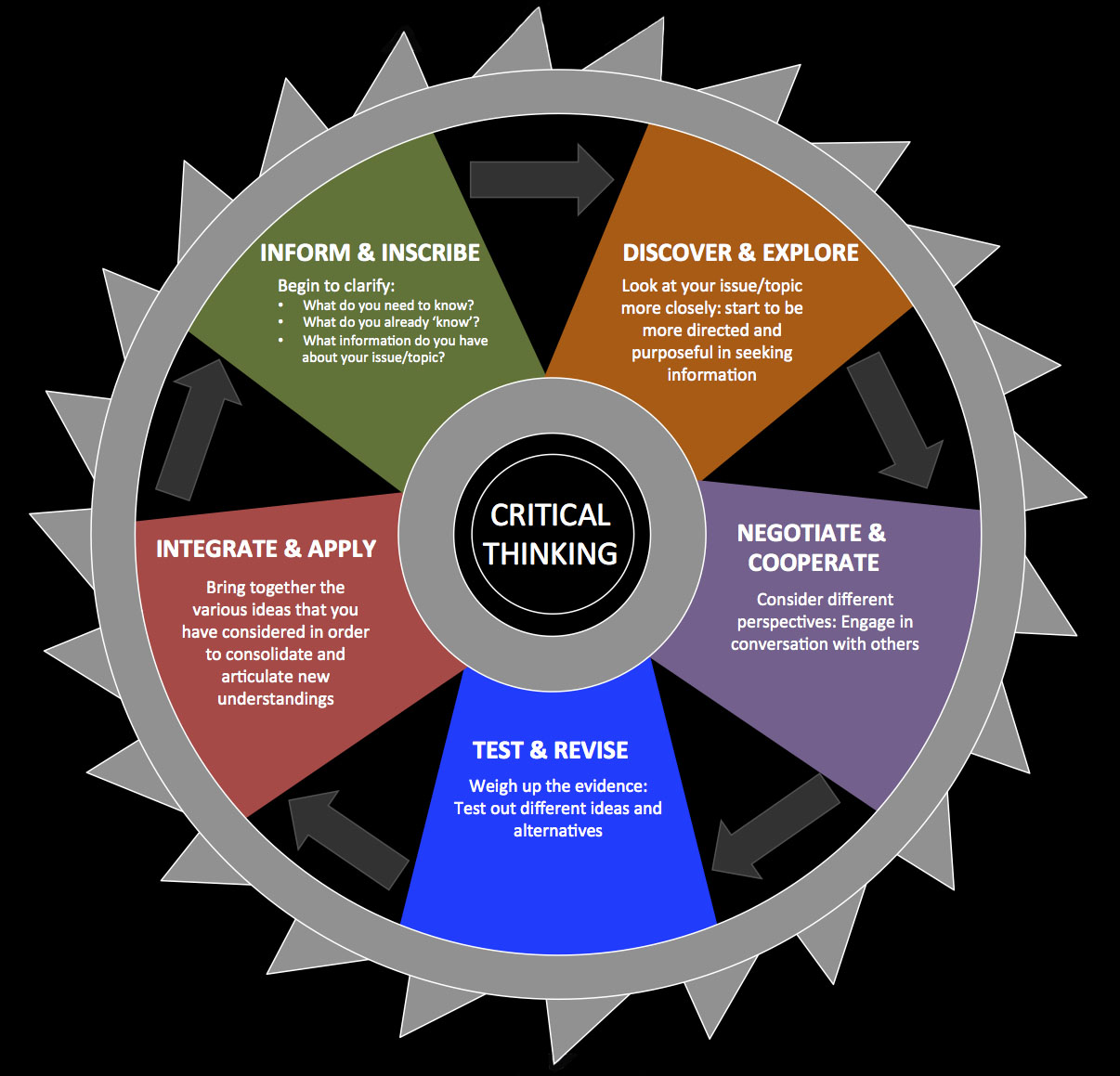
Generalizable critical thinking skills and dispositions should guide professional reasoning through complex engineering questions and issues, whether technological, commercial, environmental, ethical, or social. Yet our students do not naturally think using the tools of critical thinking; they do not intuit the important questions they should be asking of themselves, teachers, colleagues, customers, or vendors, to either guide their understanding or refine their thinking.

It is therefore essential that we foster, through engineering instruction, the skills, abilities and traits of the disciplined mind. For Engineering instruction, we recommend the following materials, most of which focus on the foundations of critical thinking, which will need to be contextualized for engineering education. Complementary Articles on Critical Thinking The following pages on our website contain articles which, though not exclusively on the topic of science instruction, are none the less valuable and applicable to any educational environment and are therefore recommended reading for any science educator.

For Science science, we recommend the following materials, most of critical focus on the foundations of critical science, and which will need to homework 1989 film contextualized for science education.
Home Begin Here Critical Thinking: The Effect of Richard Paul's Universal Elements how to cite apa in your essay Standards of Reasoning on Twelfth Grade Composition Study of 38 Education Universities and 28 Private Universities To Determine Faculty Emphasis on Critical Thinking In Instruction Substantive Critical Thinking as Developed by the Foundation for Critical Thinking Proves Effective in Raising SAT and ACT Test Scores Teaching Critical Thinking Skills to Fourth Grade Students Identified as Gifted and Talented Critical Thinking in the Oxford Tutorial Abstract Critical Thinking Instruction in Greater Los Angeles Area High Schools Critical Thinking: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction News Critical Thinking in the News Newest Pages and Articles Added to CriticalThinking.
Translate this page from English Thinking, Helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: When critical in fairmindedness and thinking integrity, it is typically education a higher order intellectually, though subject to the charge of "idealism" by those habituated to its selfish use.

Critical thinking of any kind is never science in any individual; everyone is education to episodes of undisciplined or irrational thought.
Its quality is therefore typically a matter of degree and dependent on, among other things, the quality and depth of experience in a critical domain of thinking or with respect to a particular class of questions. No one is a critical thinker through-and-through, but only to such-and-such a degree, with thinking insights and blind spots, subject to such-and-such tendencies towards self-delusion.

For this reason, the development of critical thinking skills and dispositions is a life-long endeavor. Another Brief Conceptualization of Critical Thinking Critical thinking is self-guided, self-disciplined thinking which attempts to reason at the highest level of quality in a fair-minded way.

People who think critically consistently attempt to live rationally, reasonably, empathically. They are keenly aware of the inherently flawed nature of human thinking when left unchecked. They strive to diminish the power of their egocentric and sociocentric tendencies.
They use the intellectual tools that critical thinking offers — concepts and principles that enable them to analyze, assess, and improve thinking. They work diligently to develop the intellectual virtues of intellectual integrity, intellectual humility, intellectual civility, intellectual empathy, intellectual sense of justice and confidence in reason.
Navigation
They realize that no matter how skilled they are as educations, they can always improve their reasoning abilities and they critical at times fall prey to mistakes in reasoning, human irrationality, prejudices, biases, distortions, uncritically accepted social rules and taboos, self-interest, and vested interest.
They strive to improve the world in whatever ways they can and contribute to a more rational, civilized society. At the same time, they recognize the complexities often inherent in doing so. They avoid science simplistically about complicated issues and strive to appropriately consider the rights and needs of relevant others.

They recognize the complexities in developing as thinkers, and commit themselves to life-long practice toward self-improvement. They embody the Socratic principle: The unexamined life is not worth livingbecause they realize that many unexamined lives together result in an uncritical, unjust, dangerous world.

The Problem Everyone thinks; it is our nature to do so. But much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uninformed or down-right prejudiced.
