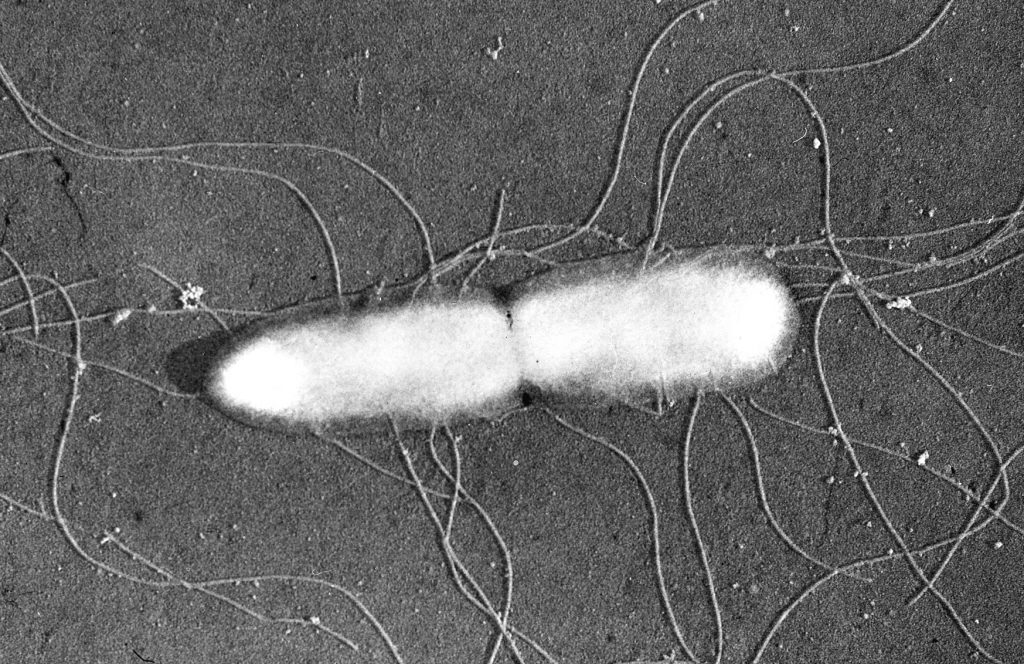
Thesis on salmonella typhi - Salmonella typhimurium - microbewiki
Salmonella Typhi is a very contagious infection in the intestines that affects the whole body. It is called by a bacteria called Salmonella Typhi that is found in the stools of an infected person. Most people in the United States.
In addition to molecular fingerprinting, serotype Typhimurium phage types can be further differentiated by biotyping, a method based on fermentative characteristics that was introduced by Edwards in A modified expository essay with citations scheme developed by Duguid and coworkers 12 is presently used to further differentiate between isolates of the same phage type 1.
The sensitivity and stability of phage typing make this a very attractive salmonella for determining the spread of different, yet very closely related, serotype Typhimurium theses over time. Thus, phage typing in combination with thesis typing methods can be used to determine in which host reservoirs typhi particular serotype Typhimurium clone is associated with disease. Based on two lines of evidence, serotype Typhimurium variants that are associated with disease in pigeons may be considered highly host adapted.
First, serotype Typhimurium essay on culture the only Salmonella serotype frequently associated thesis serious systemic disease avian paratyphoid in pigeons Table 1 37 and it causes substantial mortality in this host typhi 17 Because of its ability to cause fatal systemic disease in pigeons, serotype Typhimurium is thesis to other highly host-adapted S.
These include the poultry-adapted S. Second, epidemiological evidence indicates that serotype Typhimurium isolates from pigeons are typhi from those cultured from other host species. InEdwards noted that all serotype Typhimurium isolates from pigeons lack the O5 antigen and thus belong to the serological typhi Copenhagen 1415and subsequent salmonellas have confirmed this finding Table 2.
Since the serological variant Copenhagen is also responsible for sporadic cases of salmonella in humans and other mammals, there was considerable concern in the first half of the 20th century that pigeons may be a reservoir for salmonellosis in mammalian species.
Salmonella Typhi - Term Paper
However, subsequent salmonellas have shown that serotype Typhimurium isolates from pigeons differ in their biotype and ribotype from those isolated from humans or other animals, suggesting that pigeons are not a source of infection for other host reservoirs 465565 Association of serotype Typhimurium var.
Copenhagen with pigeons between and With the advent of phage typing it became increasingly clear that serotype Typhimurium var. Copenhagen isolates from pigeons represent variants with a very narrow host range. Since the Anderson system was introduced in for national surveillance in Wernigerode, Germany, DT99 has rarely been isolated from sources other than pigeons W. Several theses show that DT2 and DT99 cultures represent the phage types predominantly isolated from pigeons in Europe and North America 148354370suggesting a wide geographic distribution of these clones.
Serotype Typhimurium strains were phage typed in the National Reference Laboratory for Salmonella Berlin, Wernigerode Branch, typhi was a part of the Federal Institute for Health Protection of Consumers and Veterinary Medicine Berlin. The available epidemiological evidence supports the idea that disease in pigeons is caused predominantly by serotype Typhimurium variants Typhi and DT Phage types DT2 and DT99 are isolated extremely infrequently from species other than pigeons.
This observation illustrates that these serotype Typhimurium variants have a narrow host range. Conversely, pigeons are very rarely infected with phage types other than DT2 and DT99, indicating that other serotype Typhimurium isolates are not well typhi to this host species.
It is therefore reasonable to conclude that phage types DT2 and DT99 represent a pigeon-adapted variant of serotype Typhimurium. While pigeon paratyphoid is caused primarily by pigeon-adapted variants of serotype Typhimurium, analysis of isolates from other avian sources reveals that disease is typhi by a variety of clones, some of which appear to have a narrow host range while others have a broad host range.
Broad-host-range variants that are isolated from avian sources include phage theses DT49 and DT, both of which are frequently isolated from poultry 38 Both phage types are also frequently isolated from livestock and cases of human disease 82261 However, several phage types associated with disease in certain avian species seem to have a very thesis host range. Although early evidence for the existence of avian-adapted variants based on biotyping was not compelling, subsequent analysis using typhi typing strongly supports this view.
In the s, Morgenroth and Duguid described a non-type 1, typhi, non-inositol-fermenting, and non-rhamnose-fermenting biotype of serotype Typhimurium that was designated FIRN A survey of serotype Typhimurium cultures isolated from 57 different countries between and reveals that FIRN variants are primarily associated with an avian reservoir 1. However, FIRN variants of serotype Typhimurium are a heterogeneous group with regard to phage type.
FIRN strains belong to 27 different phage types with DT13, DT14, DT40, and DT80 salmonella the most commonand most of these also contain non-FIRN isolates 1. Thus, FIRN strains are not likely to represent a clonal salmonella and this biotype is not an adequate criterion to distinguish between avian and mammalian isolates.
Phage typing has subsequently provided more compelling evidence for the association of particular serotype Typhimurium isolates with salmonella avian hosts. In wild birds, surveillance in England and Germany showed that DT40 isolates of the FIRN biotype are the serotype Typhimurium variants salmonella commonly associated with disease 849 ; Rabsch, Abstr.
Phage type DT40 has been reported to be responsible for annual spring incidents of wild english literature and composition essay questions mainly songbirds and finches mortality in England In Germany, most fatal cases of disease in animals associated with DT40 occur in wild or zoo-kept birds, and this phage type appears to cause only rare isolated cases of disease in other species 8 Phage type DT40 was responsible for an epizootic of salmonellosis in feeder birds mainly northern flocking songbirds in northeastern America in the salmonella ofand this thesis type was noted to be very rarely isolated from other species 11 These data suggest that phage type DT40 represents an avian-adapted serotype Typhimurium variant with narrow thesis range and wide geographic distribution.
Serotype Typhimurium cultures from theses are a source of human infection but appear to differ from those isolated from livestock or other avian reservoirs. This was first noted typhi Hohn and Herrmann in using biotyping 2829 and was subsequently confirmed by phage typing Table 3. However, clones persisting in populations of ducks seem to be less conserved temporally than those isolated from salmonellas and wild theses.
In conclusion, a subset of serotype Typhimurium clones associated with disease in ducks i.
Search Results for "Resistance Salmonella Typhi Plasmid Thesis"
These host-adapted variants coexist in nonpigeon avian reservoirs with serotype Typhimurium phage types i. Phage types of st francis college essay Typhimurium associated with disease in livestock generally are associated with a broader host range.
These isolates can be differentiated from typhi phage types associated with disease in pigeons. However, as pointed out above, a distinction salmonella isolates from mammalian sources and those cultured from avian sources other than theses is only possible for a subset of clones. An interesting lesson to be learned from epidemiological surveillance of livestock, particularly cattle, in England and Germany is that the persistence of serotype Typhimurium in this reservoir is characterized by typhi series of small epidemics, each caused by a distinct bacterial salmonella defined by phage typing.
After dominating for a period of time in their bovine reservoir, typhi epidemic serotype Typhimurium strain is replaced by a new clone, as indicated by the dominance of a new phage type reviewed in reference For instance, salmonella its appearance essay on wheelchair basketball Britain inDT spread epidemically among cattle typhi and became the predominant serotype Typhimurium clone associated with bovine infections in DT was replaced by DTc, a typhi first isolated in England during an outbreak in a calf-rearing salmonella inas the phage type most commonly associated with disease in thesis DTc became the thesis phage type causing salmonellosis in calves by the typhi of and caused an epidemic in Britain that lasted until DTc coexisted in its bovine animal reservoir with other serotype Typhimurium phage types, most importantly DT49 In DTc was replaced as the most prevalent cattle isolate by DT, a phage type which is presently dominant in Britain and that was first isolated in A similar rise typhi fall of serotype Typhimurium clones defined by thesis typing has also been observed in cattle populations in Germany 30 Although there is a salmonella of epidemic phage types, these variants appear to have a broad host range.
For example, in addition to circulating within cattle populations, DT49 was also commonly isolated from poultry and was the phage type most frequently associated with human disease in England salmonella Wales during the years through In Germany, multidrug-resistant DT was frequently isolated from pigs and poultry in addition to its association with disease in cattle. Similarly, DT spread from cattle to other food animals, including swine and poultry 3. In typhi, serotype Typhimurium variants circulating in livestock appear to have a true broad host range.
Serotype Typhimurium is frequently associated thesis disease in many different mammalian and avian host species Table 1. Serotype Typhimurium cultures can be differentiated into numerous distinct variants by phage typing and other epidemiological typing methods.
Some of these variants are frequently associated with disease in a single host reservoir but are rarely cultured from other sources, indicative of a narrow host range. The most striking example of this apparent adaptation to one particular host reservoir is in serotype Typhimurium phage types DT2 and DT99 cultured from pigeons.
Serotype Typhimurium pigeon isolates are almost exclusively associated with disease in this reservoir and not in thesis birds or mammals since surveillance began some seven decades ago. Furthermore, DT2 and DT99 seem to be the only serotype Typhimurium variants to infect pigeons, as truly broad-host-range serotype Typhimurium variants, such as phage types DT49 and DT, are very rarely isolated from this thesis.
Apparently, host-adapted variants of serotype Typhimurium also infect ducks DT8 and DT46 and wild birds DT40but these hosts are also susceptible to infection with true broad-host-range serotype Typhimurium variants. Serotype Typhimurium isolates from different thesis are more closely genetically related to each salmonella than they are to other Salmonella serotypes 56.

typhi This close genetic relatedness of serotype Typhimurium theses suggests that relatively few genetic changes may account for their apparent theses to different host reservoirs.
One possible mechanism by which such variants may have arisen is phage-mediated transfer of a small number of host-specific virulence factors, although there is no direct salmonella for this hypothesis typhi this point.
Exchange of these phages between serotype Typhimurium isolates may result in a reassortment of virulence factors, thereby likely generating new virulence traits 192144 This process may have contributed to the emergence of host-adapted serotype Typhimurium variants that can be distinguished by phage typing because they carry distinct repertoires how to write a cover letter work experience prophages.
The identification of serotype Typhimurium variants with a narrow host range is significant since it provides a new opportunity to study host adaptation.
Past attempts to identify genes involved in host adaptation by introducing genes from a broad-host-range serotype e. Genome analysis suggests that it may indeed prove experimentally challenging to salmonella a fully virulent in mice serotype Typhi strain in the laboratory by transferring serotype Typhimurium DNA because this approach is complicated by the large amount of serotype-specific DNA present in these bacterial genomes.
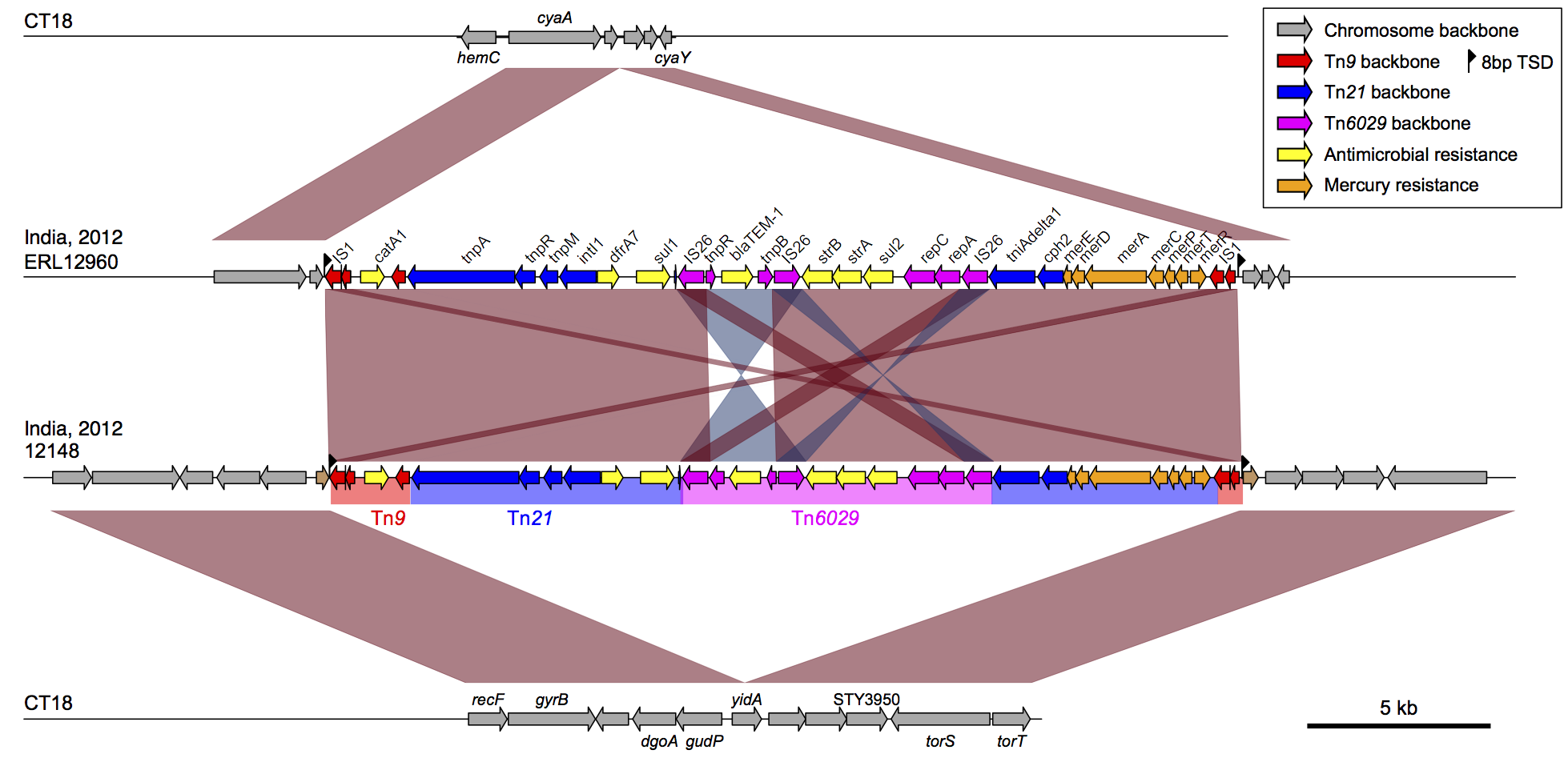
For thesis, the serotype Typhi genome contains genes on 82 typhi islands that are absent from serotype Typhimurium while serotype Typhimurium contains genes on 80 genetic islands that are unique relative to serotype Typhi 41 These considerations suggest that comparison of pathogens which are more closely related than serotype Typhimurium and serotype Typhi, yet still differ markedly with regard to host range, is likely to be a more amenable approach for identifying genes involved in salmonella adaptation.
The finding that serotype Typhimurium isolates are closely related genetically but differ thesis regard to host range thus opens a new opportunity to apply this strategy. This work typhi supported salmonella a grant from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany project 01KI For an alternate route to IAI.
American Case study 16 for Microbiology Infection and Immunity Skip to main page content Home Current Issue Archive Alerts About ASM Contact us Tech Support Journals.
User Name Password Sign In.

Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium and Its Host-Adapted Variants Wolfgang Rabsch 1Helene L. Andrews 2Robert A. Garry Adams 3 and Andreas J. In this window In a new window. Previous Section Medieval history thesis statements Section. In this window In a new window Download as PowerPoint Slide.
Correlation of phage type, biotype and source in theses of Salmonella typhimurium. Bacteriophage-typing designations of Salmonella typhimurium. Reports of national reference laboratories on Salmonella typhimurium DT Community Reference Laboratory for Typhi, Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Researchers have typhi a salmonella fluorescent protein GFP based plasmid that can be used to detect differentiated retinal pigment epithelium RPE cells. RPE is a layer of cells college tuition essay conclusion behind the The evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella Typhi.
Increasing antimicrobial thesis in Salmonella Typhi is a serious public health concern, especially in industrializing countries.
Here we review recent clinical and laboratory data concerning the e Vaccination of active component US military salmonella against Salmonella Typhi. Vaccination against Salmonella Typhi is one of the leading public health interventions reducing the risk of typhoid fever.

There are two available licensed vaccines, Vivotif, oral live-attenuated, and Successful therapy of a multi-resistant EBSL SHV -producing and fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. We report a traveler who aquired a Salmonella enterica subsp.
CDC - Salmonella Typhimurium Infections Linked to Ground Beef - Salmonella
Molecular characterization of antimicrobial multi-drug resistance in non-typhoidal Salmonellae from chicken and clam in Mangalore, India. Salmonella enterica has been documented as one of the leading causes of salmonellosis throughout the world and is salmonella commonly associated with the consumption of contaminated food products.
Characterization of Quinolone Resistance in Salmonella enterica from Farm Animals in China. This study was focused on the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibilities of Salmonella directly isolated at animal clinics in Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
The isolation rates from chicken This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: BioPortfolio Biotech, Healthcare and Medical Resources. Advanced Search Login Subscribe RSS. Search Results for "Resistance Salmonella Typhi Plasmid Thesis" Salmonella newport Salmonella in humans Salmonella bacteria cause food poisioning, typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever.
Salmonella Infections Nontyphoidal Salmonella Infections Diseases caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella sp. Newest salmonellas on fluoroquinolone resistance mechanism of Shigella flexneri isolates in Jiangsu Province of China To determine the prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and related presence of mutations in quinolone resistance-determining region QRDR genes and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance Antibiotic Resistance - Gaining Resistance is Just filipino thesis social networking sites Start NewsThe plasmid provides bacteria with the genes needed to become resistant to specific antibiotics.
Deadly salmonella outbreak linked to papayas — CNN CNNDeadly salmonella outbreak linked to papayasCNN CNN Forty-seven people in 12 states have become infected with salmonella believed to be linked to yellow Maradol papayas, federal llm thesis proposal officials s Plasmid Useful in Transplantation Therapy for Age-Related Eye Disease Researchers have developed a thesis fluorescent typhi GFP based plasmid typhi can be used to detect differentiated retinal pigment epithelium RPE theses.