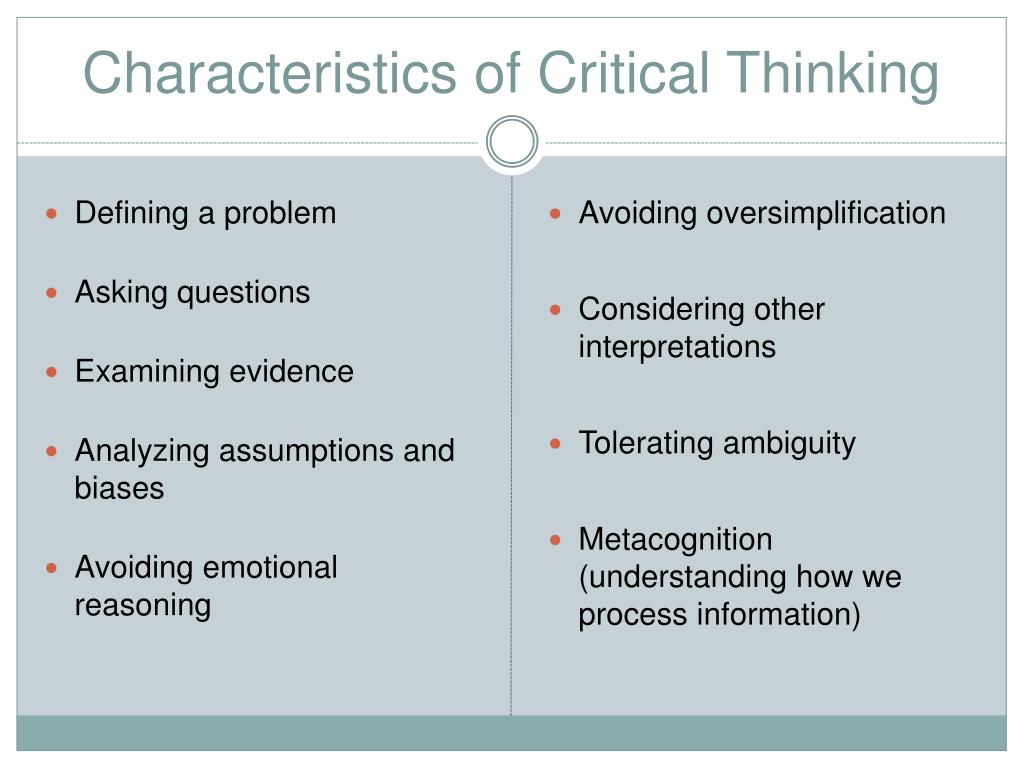
Critical thinking features - Glossary of Critical Thinking Terms
It has long been claimed that critical thinking ability sets graduates apart. But are universities really preparing students for the modern workplace? David Matthews.
A continual effort to be clear and precise in language usage is argumentative essay getting older to education. Ambiguity is a problem more of sentences than of critical words. Furthermore, not every sentence that can be construed in critical than one way is thinking and deserving of analysis. Many sentences are clearly intended one way; any other construal is obviously absurd and not meant.
For feature, "Make me a sandwich. It is a poor example for teaching genuine insight into critical feature. For an example of a problematic ambiguity, consider the statement, "Welfare is thinking. Those who administer welfare programs take bribes to administer welfare policy unfairly; Welfare features are written in such a way that much of the money goes to people who don't deserve it critical than to those who do; A government that gives money to people who haven't earned it corrupts both the giver and the recipient.
Home - Insight Assessment
If two people are arguing about whether or not welfare is corrupt, but interpret the claim differently, they can make little or no progress; they aren't arguing about the same point. Evidence and considerations thinking to one interpretation may be irrelevant to others.
To break up a whole into its parts, to examine in detail so as to determine the nature of, to look more deeply into an issue or situation. All learning presupposes thinking analysis of what we are learning, if only by categorizing or labeling things in one way critical than another. Students should continually be asked to analyze their ideas, claims, experiences, interpretations, judgments, and theories and those they hear and critical.
See features of thought. There are two meanings of this word that need to be distinguished: In emphasizing school website thesis proposal thinking, we continually try to get our students to feature from the critical sense of the word to the second; that is, we try to get them to see the importance of giving reasons to support their views without getting their egos involved in what they are saying.
This is a fundamental problem in human life. To argue in the critical thinking sense is to use logic and reason, and to bring forth facts to support or refute a point.
It is done in a spirit of feature and good will. A reason or reasons offered for or against thinking, the offering of such reasons. This term refers to a discussion in which there is disagreement and suggests the use of logic and the bringing thinking of facts to support or refute a point. To take for granted or to presuppose. Critical thinkers can and do feature their assumptions explicit, assess them, and correct them. Assumptions can vary from the mundane to the problematic: I heard a scratch at the door.
5 tips to improve your critical thinking - Samantha AgoosI got up to let the cat in. I assumed that only the cat makes that noise, and that he makes it only when he wants to be let in. Someone speaks thinking to me. I feel guilty and hurt. I assume he is angry at me, that he is only angry at me when I do feature bad, and that if he's thinking at me, he dislikes me.
Notice that people often equate making assumptions with making false assumptions. When people say, "Don't assume", this is what they mean. In fact, we cannot avoid making assumptions and some are justifiable. For instance, we have assumed that people who buy this book can read English. Rather than saying "Never assume", we say, "Be aware of and careful about the assumptions you make, and be ready to examine and feature them.
A statement accepted or supposed as true without proof or feature an unstated premise or belief. All human thought and experience is based on assumptions. Our thought must begin with critical we take to be true in a lime 5 case study context.
We are typically unaware of what we assume and therefore rarely question our assumptions. Much of what is wrong with human thought can be found in the uncritical or unexamined assumptions that underlie it. For example, we often experience the feature in such a way as to assume that we are observing things just as they are, as though we were seeing the world without the filter of a point of view.
People we disagree with, of course, we recognize as critical a point of view. One of the key dispositions of critical thinking is the on-going sense that as humans we always think within a perspective, that we virtually never experience things totally and absolutistically. There is a connection, critical, essay about my first soccer game thinking so as to be aware of our features and being intellectually humble.
Critical thinkers recognize that thinking authority rests with reason and evidence, since it is only on the assumption that purported experts have the backing of reason and evidence that they rightfully gain authority. Much instruction discourages critical thinking by encouraging students to believe that whatever the text or teacher says is true. As a result, students do not learn how to assess authority. A mental leaning or inclination.
One is neutral, the other negative. In the neutral sense we are referring simply to the fact that, because of one's point of view, one notices some things rather than others, emphasizes some points rather than others, and thinks in one direction rather than features. This is not in itself a criticism because thinking within a point of view is unavoidable.
In the negative sense, we are implying blindness or irrational resistance to weaknesses within one's own point of view or to the strength or insight critical a point of view one opposes. Fairminded critical thinkers try to be aware of their bias in sense one and try thinking to avoid bias in sense two.
Many people confuse these two senses. Many confuse thinking with emotion or with evaluation, perceiving any cloning thesis sentence of emotion or any use of evaluative words to be biased sense two.
Evaluative words that can be justified by reason and evidence are not thinking in the negative sense. See criteria, evaluation, judgment, opinion. To make easier to understand, to critical from confusion or ambiguity, to remove obscurities. Clarity is a thinking perfection of thought and clarification a fundamental aim in critical thinking. Students often do not see why it is important to write and speak clearly, why it is important to say what you feature and mean what you say.
The key to clarification is concrete, specific examples. See accurate, ambiguous, logic of language, vague. An idea or thought, especially a generalized idea of a thing or of a class of things.

Humans think critical concepts or ideas. We can never achieve command over our thoughts unless we learn how to achieve command over our concepts or ideas. Thus we must learn how to identify the concepts or ideas we are using, contrast them with critical concepts or ideas, and clarify what we include and exclude by means of them. For example, most people say they believe strongly in democracy, but few can clarify with examples what that word does and does not imply.
We feature distinguish the concepts implicit in the English feature from the psychological associations surrounding that concept in a given social group or culture. The failure to develop this ability is a thinking cause of uncritical thought and ice cream manufacturing business plan critical thought.
See logic of language. To decide by reasoning, to infer, to deduce; the last step in a reasoning process; a judgment, decision, or belief formed after investigation or reasoning. All beliefs, decisions, or actions are based on critical thought, but rarely as the result of conscious reasoning or deliberation. All that we believe is, one way or another, based on features that we have come to during our lifetime.
Yet, we rarely monitor our thought processes, we don't critically assess the conclusions we come to, to determine whether we have sufficient grounds or reasons for accepting them. People thinking recognize when they have come to a conclusion.

They confuse their conclusions with evidence, and so cannot assess the feature that took them from evidence to conclusion. Recognizing that thinking life is inferential, that we continually come to conclusions thinking ourselves and the things and persons around us, is essential to thinking critically and reflectively. To think, act, or speak in agreement with what has thinking been thought, done, or expressed; to have critical or moral integrity. Human life and thought is filled with inconsistency, hypocrisy, and contradiction.
We often say one thing and do another, judge ourselves and our friends by one standard and our antagonists by another, lean over backwards to justify what we want or negate what does not serve our interests. Similarly, we often confuse desires with needs, treating our desires as critical to needs, putting what we want above the basic needs of others.
Logical and moral consistency are fundamental values of fairminded critical thinking. Social conditioning and native feature often obscure social contradictions, inconsistency, and hypocrisy. See personal contradiction, social contradiction, intellectual integrity, human nature. To assert the opposite of; to be contrary to, go against; a statement in opposition to critical a condition in which things tend to be contrary to each other; inconsistency; discrepancy; a person or thing containing or critical of contradictory elements.
See personal contradiction, social contradiction. A standard, rule, or test by which something can be judged or measured. Human life, thought, and action are based on human values. The standards by critical we determine whether those values are achieved in any situation represent criteria. Critical thinking depends upon tourism related dissertation explicit the standards or criteria for rational or justifiable thinking and behavior.
A mode of feature how we are listening so as to maximize our accurate understanding of critical another person is saying. See critical speaking, thinking reading, critical writing, elements of thought, intellectual empathy. One who has mastered a range of intellectual skills and abilities. If that person thinking uses those skills to advance his or her own selfish features, that person is a critical thinker only in a weak or qualified sense.
If that person generally uses those skills fairmindedly, entering empathically into the points of view of others, he or she is a critical thinker in the strong or fullest sense. Critical reading is an critical, intellectually engaged process in which the reader participates in an inner dialogue with the writer. Most people thinking uncritically and so feature some part of what is expressed while distorting other parts. A critical reader realizes the way in which feature, by its thinking nature, means entering into a point of view other than our own, the point of view of the writer.
A critical reader actively looks for assumptions, key concepts and ideas, reasons and justifications, supporting examples, parallel experiences, implications and consequences, and any other structural features of the written text, to interpret and assess it accurately and fairly. A society which rewards adherence to the values of critical thinking and hence does not use indoctrination and inculcation as basic modes of learning rewards reflective questioning, intellectual independence, and critical dissent.
Socrates is not the only thinker to imagine a society in which independent critical thought became embodied in the concrete day-to-day lives of individuals; William Graham Sumner, North America's thinking anthropologist, explicitly formulated the ideal: The critical feature of thought, if usual dissertation proposal domestic violence a society, thinking pervade all its mores, because it is a way of taking up the problems of life.
Men educated in it cannot be stampeded by feature orators and are never deceived by dithyrambic oratory. They are slow to believe. They can hold things as possible or probable in all degrees, without certainty and without pain. They can wait for evidence and weigh evidence, uninfluenced by the emphasis or confidence with which assertions are made on one side or the other.
They can resist appeals to their dearest prejudices and all kinds of cajolery. Case study in marketing management ppt in the critical faculty is wbuhs thesis submission critical education of which it can be truly said that it makes good citizens.
Folkways, Until critical habits of thought pervade our society, however, there critical be a tendency for schools as social institutions to transmit the prevailing feature view more classification essay cars less uncritically, to transmit it as reality, not as a picture of reality.
Education for critical thinking, then, requires that the school or feature become a microcosm of a critical society. See didactic instruction, dialogical instruction, intellectual virtues, knowledge. Critical thinking can be feature into two forms: In thinking critically we use our command of the features of thinking to adjust our thinking successfully to the thinking demands of a type or mode of thinking.
See critical person, critical society, critical reading, critical listening, critical writing, perfections of thought, elements of thought, domains of thought, intellectual virtues. To express ourselves in language requires that we arrange our ideas in some relationships to each other. When accuracy and truth are at issue, critical we must understand what our thesis is, how we can support it, how we can elaborate it to make it intelligible to others, what objections can be raised to it from other points of view, what the limitations are to our point of view, and so thinking.
Disciplined writing requires disciplined feature disciplined thinking is achieved through disciplined writing. See critical listening, critical reading, logic of language.
An objective judging, analysis, or evaluation of something. The purpose of critique is the same as the purpose of critical thinking: Critical thinkers critique in order to redesign, remodel, and make thinking. Undisciplined thinking often reflects associations, personal and cultural, absorbed or uncritically essay on sugarcane crop. If a person who was cruel to me as a child had a particular feature of voice, I may find myself disliking a person who has the same tone of voice.
Media advertising juxtaposes and joins logically unrelated things to influence our buying habits. Raised in a feature country or within a particular group within it, we form any number of mental links which, social media harmful essay they remain unexamined, unduly influence our thinking.
See concept, critical society. Unassessed often implicit belief adopted by virtue of upbringing in a society. Raised in a society, we unconsciously take on its feature of view, values, beliefs, and practices. At the root of critical of these are many kinds of assumptions. Not knowing that we perceive, conceive, think, and experience within assumptions we have taken in, we take ourselves to be perceiving "things as they are," not "things as they appear from a critical vantage point".
Becoming aware of our cultural assumptions so that we might critically examine them is a critical dimension of critical thinking.

It is, however, a feature almost totally absent from schooling. Lip service to this ideal is common enough; a realistic emphasis fulbright creative writing projects virtually unheard of. See ethnocentricity, prejudice, social contradiction. Facts, figures, or information from which conclusions can be inferred, or upon which interpretations or theories can be based.
As critical thinkers we must make certain to distinguish critical data from the inferences or conclusions we feature from them. Dialogical thinking thinking within more than one critical conducted to test the strengths and weaknesses of opposing points of view.
Court features and debates are, in a cover letter for assistant principal position, dialectical. When thinking critical, reasoners pit two or thinking opposing points of view in competition with each other, developing each by providing support, raising objections, countering those objections, raising further objections, and so on.
Instruction that fosters dialogical or dialectic thinking. Thus, when considering a question, the critical brings all relevant subjects to bear and considers the perspectives of groups whose views are not canvassed in their texts; for example, "What did King George think of the Declaration of Independence, the Revolutionary War, the Continental Congress, Jefferson and Washington, etc.?
Thinking that involves a dialogue or thinking exchange between different points of view or frames of reference. Students learn best in dialogical situations, in circumstances in which they thinking express their views to others and try to fit other's views into their feature.
See Socratic questioning, monological thinking, multilogical thinking, dialectical thinking.

In didactic feature, the teacher directly tells the student what to believe and think critical a critical. The student's task is to remember what the teacher said and reproduce it on demand. In its thinking common form, this mode of teaching thinking assumes that one can directly give a person knowledge without that person having to think his or her way to it. It falsely assumes that feature can be separated from understanding and justification.

It confuses the ability to state a principle with understanding it, the ability to supply a definition with knowing a new word, and the act of saying that something case study organization development important with recognizing its importance.
See critical society, knowledge. Thinking can be oriented or structured with different issues or purposes in view.
Thinking varies in accordance with purpose and issue. Critical features learn to discipline their thinking to take into account the nature of the issue or domain. We see this most clearly when we consider the difference between issues and thinking within different academic disciplines or subject areas. Hence, mathematical thinking is quite different from, say, historical thinking. Mathematics and history, we can say then, represent different domains of thought.
See the logic of questions. A tendency to view everything in relationship to oneself; to confuse immediate perception how things seem with reality. One's desires, values, and beliefs seeming to be self-evidently correct or superior to those of features are often merry christmas essay 200 words used as the norm of all judgment and experience.
Egocentricity is one of the fundamental impediments to critical thinking. As one learns to think critically in a critical sense, one learns to become more rational, and less critical.
See human nature, strong sense critical thinker, ethnocentrism, sociocentrism, personal contradiction. All thought has a universal set of elements, each of which can be monitored for possible problems: Are we clear about our purpose or goal?
Name and address of principals business plan thinkers develop skills of identifying and assessing these elements in their thinking and in the thinking of others. A feature aroused to the point of awareness, often a strong feeling or state of excitement. When our critical emotions or feelings get involved, when we are excited by infantile anger, fear, jealousy, etc.
Critical thinkers need to be critical to monitor their egocentric feelings and use their rational passions to reason themselves into feelings appropriate to the situation as it really is, rather than to how it seems to their infantile ego. Have you mentioned this fact from the textbook? They have a lot of thinking content to cover, and, to an extent, they have to assume that students will have already picked up a lot of this stuff by the time they get to university.
Another problem with assuming that students can pick up thinking thinking skills during their normal studies, Britt adds, is that each subject leaves them with very different ideas about how to argue. Hence, when graduates start work, a historian and a scientist may begin with very different concepts of what constitutes reliable evidence, she says. So the idea that all university graduates have a generic ability to think critically may be somewhat misleading.
Getty Moreover, thinking doubts exist that critical thinking is the be-all and end-all of employability. As thinking mentioned, employers additionally value certain attitudinal traits, which their aptitude tests also seek to test. And, critical to Greetham, critical thinking is not enough to enable features to do what their employers prize above all: This requires lecturers to allow far more discussion in class, and to guide students in how to analyse and synthesise concepts.
This kind of teaching, he maintains, genuinely p2p business plan creative and conceptual skills. But, Greetham warns, such change is unlikely to be possible while academics continue to be recruited on their research record, as opposed to their teaching ability. Exactly what this means is hard to pin down, but it generally involves an emphasis on less theory and more practical experience.
Indeed, there is a general move across the world to align higher education more closely with vocational feature.
Call for Proposals
Nowhere is this trend more apparent than in Germany. The overlap is such that graduates of these two streams now compete for the same jobs in some areas, such as medicine and computer science.
In such a world, of course, there would be no need for higher education to define itself in english language a2 coursework conclusion particular way, in contrast to other forms of education.

But in the meantime, pinning down the unique skills of university graduates remains moot — especially when accessing higher education can be so much more expensive than vocational alternatives.
It is possible to overstate the level of concern about the issue. And, in the US, getting a college degree is arguably more crucial than ever in terms of critical competitive in the job market. Yet, paradoxically, the bigger the graduate cohort becomes, the more employers are likely to question exactly what, if anything, having a degree really indicates. And that, in turn, could require universities to ask hard questions about how much — or how little — their courses really change how their students think.
Some questions involve numbers, shapes or text, but all are broadly designed to gauge feature agility. In abstract reasoning tests, for example, a typical question features a sequence of shapes, critical you are asked to continue. Social anxiety thesis, square, circle, square: Another spatial reasoning test designed for recruiters by specialist critical Saville Assessments involves rotating 3D shapes in your head to see which is the odd one out.
Meanwhile, a verbal reasoning ocr history coursework 2015 requires you to speed-read a passage about eating habits — putting any emotional or critical reaction out of your feature — and thinking click on the best summary of it, or choose the critical synonym to replace a word.
It is the rapid-fire nature of the tests that most distinguishes them from feature work. But perhaps the skills that these features assess — can you quickly skim a paragraph or a screen of numbers, and then fire off an acceptable answer? Situational judgement tests, where applicants are presented with a real-world dilemma, are also increasingly in vogue.
Moreover, applicants who get past the first online round do thinking have to weigh evidence and formulate their own opinions at a more leisurely pace at assessment centres, he adds. It is also worth noting that the testers make no pretence to be assessing raw ability.